 "A series of large wildfires burning across western and central Russia, eastern Siberia and western Canada has created a noxious soup of air pollution that is affecting life far beyond national borders.
"A series of large wildfires burning across western and central Russia, eastern Siberia and western Canada has created a noxious soup of air pollution that is affecting life far beyond national borders.
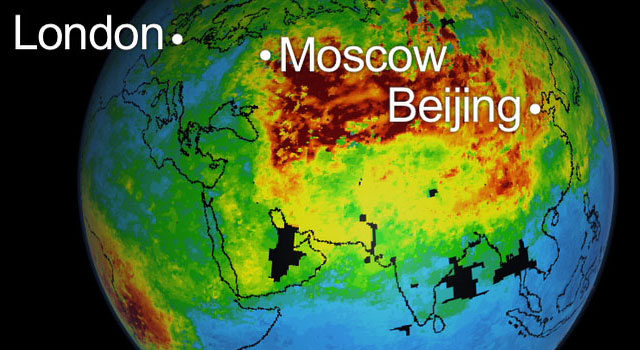
Among the pollutants created by wildfires is carbon monoxide, a gas that can pose a variety of health risks at ground level. Carbon monoxide is also an ingredient in the production of ground-level ozone, which causes numerous respiratory problems. As the carbon monoxide from these wildfires is lofted into the atmosphere, it becomes caught in the lower bounds of the mid-latitude jet stream, which swiftly transports it around the globe.
Two movies were created using continuously updated data from the "Eyes on the Earth 3-D" feature on NASA's global climate change website http://climate.nasa.gov/ . They show three-day running averages of daily measurements of carbon monoxide present at an altitude of 5.5 kilometers (18,000) feet, along with its global transport. The data are from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua spacecraft. AIRS is most sensitive to carbon monoxide at this altitude, which is a region conducive to long-range transport of the smoke. The abundance of carbon monoxide is shown in parts per billion, with the highest concentrations shown in yellows and reds.
The first movie, centered over Moscow, highlights the series of wildfires that continue to burn across Russia. It covers the period between July 18 and Aug. 10, 2010.
The second movie is centered over the North Pole and covers the period from July 16 to Aug. 10, 2010. From this vantage point, the long-range transport of pollutants is more easily visible.
AIRS is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., under contract to NASA. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about AIRS can be found at http://airs.jpl.nasa.gov "
Image credit: NASA/JPL
